What To Do When Experiencing Tooth Pain
A toothache is one of the worst kinds of pain. Toothaches can be sensitive to temperature and become even more painful when chewing or biting. The pain can be sharp or dull, depending on the nature of your toothache.
In any case, a toothache is unpleasant. And the pain can be difficult to manage on your own.
Here is why a toothache may occur and what you should do if you have tooth pain.
There are multiple reasons you may experience a toothache.
A toothache may stem from a physical injury, gum infection, cavity, abscess, or even food stuck in your teeth.
Physical Injury: Obviously, if you were to be punched in the jaw, your teeth may become damaged. But a physical injury can be less obvious, too. Maybe you play recreational sports, like basketball, and a player on the opposing team hits your face with their elbow. At first it did not hurt, but hours later you noticed the pain. Or maybe you took a bite of a hard candy and slightly chipped or otherwise damaged your tooth. These types of physical injuries can cause tooth pain.
Gum Infection: Toothaches often occur due to underlying gum infections, such as gingivitis or periodontitis. Both gum infections can damage soft tissue and destroy the bone that supports your teeth. Signs of gum disease include tooth pain, swollen gums, gums that feel tender when touched, and bleeding gums.
Cavity: A cavity is a damaged area of a tooth that develops into small holes. A cavity can form in between the time of dentist visits. You may begin experiencing tooth pain because of the cavity. The only way to repair a cavity is to have the hole filled.
Abscess: A dental abscess can result from the buildup of bacteria inside the pulp chamber. This can cause intense pain and swelling.
Food In Your Teeth: This is one of the most common causes of tooth pain. In most cases, all you need to do is floss and brush your teeth to remove the stuck food and resolve the pain. If you have sudden tooth pain, food in your teeth may be the cause!
Contact your dentist if you have persistent tooth pain.
Toothaches can vary in severity. Some toothaches are minor and can be resolved with routine brushing and flossing.
More severe toothaches can persist and do not go away for hours or days. Contact your dentist if you experience tooth pain that persists. Do not expect the pain to resolve on its own. The longer you wait for potential treatment, the worse the pain may become.
To determine the cause of your pain, a dentist will perform a routine exam. They will start by asking you questions as to the location of the pain and when the pain began. Your dentist will then check your mouth to discern if any visible signs of tooth damage exist. They may use a dental X-ray machine to take an X-ray image of your teeth, allowing them to see the whole picture.
After your dentist has determined the cause of your pain, they can set out to treat it.
Treatment depends upon the type of tooth issue you have.
- If you have a cavity, your dentist will remove the decay by drilling and replace the space with a hard filling.
- If you have advanced gum disease, your dentist may suggest removing the decayed teeth and replacing them with dental implants or dentures.
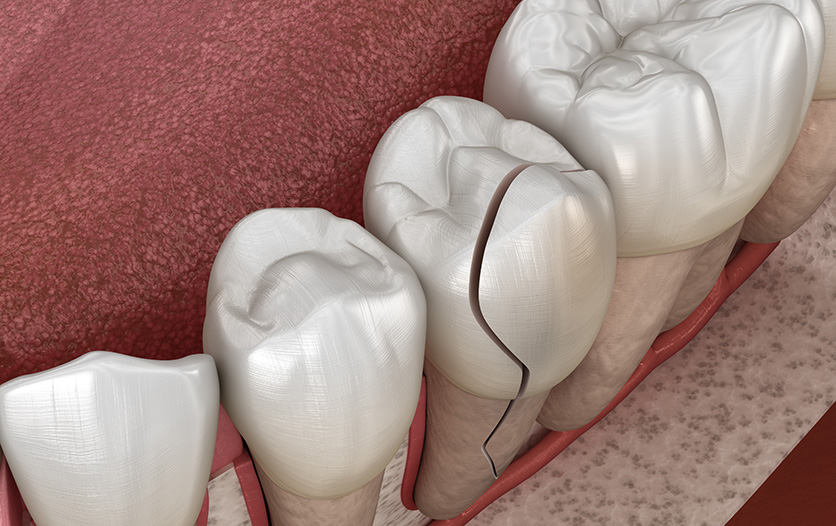
- If you have tooth damage, such as a chipped or cracked tooth, your dentist may provide a filling or suggest removing the tooth altogether.
- If you have an abscess, your dentist will make a cut in the gumline to drain the infection.
You can prevent the root causes of tooth pain by taking routine care of your teeth.
Oral hygiene is important, and good oral hygiene can go a long way in preventing tooth pain.
For good oral hygiene, you should:
- Brush twice per day with fluoride toothpaste.
- Floss twice per day.
- Visit the dentist at least twice per year, or more often if advised.
- Avoid unhealthy habits like smoking.
- Contact your dentist if you experience persistent tooth pain.
Tooth pain is no fun. It can occur suddenly and persist for days. If you have tooth pain, do not wait to contact your dentist. Tooth pain can be the sign of a more serious tooth or gum disease. As always, practice good oral hygiene to as a preventive measure.